1. Introduction ISO 9001 emphasizes documented information to maintain a quality management system (QMS). For accounting processes, this includes invoices, financial statements, cost reports, audit trails, and compliance documentation. Proper creation and management of these documents are essential for accuracy, traceability, and compliance .
2. Key Accounting Documents per ISO 9001
Financial Statements – Balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements.Invoices & Receipts – Purchase invoices, sales invoices, expense receipts.Cost Reports – Departmental costs, project costing, variance reports.Audit Records – Internal and external audit logs, review notes.Process Documentation – SOPs for accounting, procedures for approvals, and record retention schedules.Compliance Records – Tax filings, payroll records, regulatory submissions.
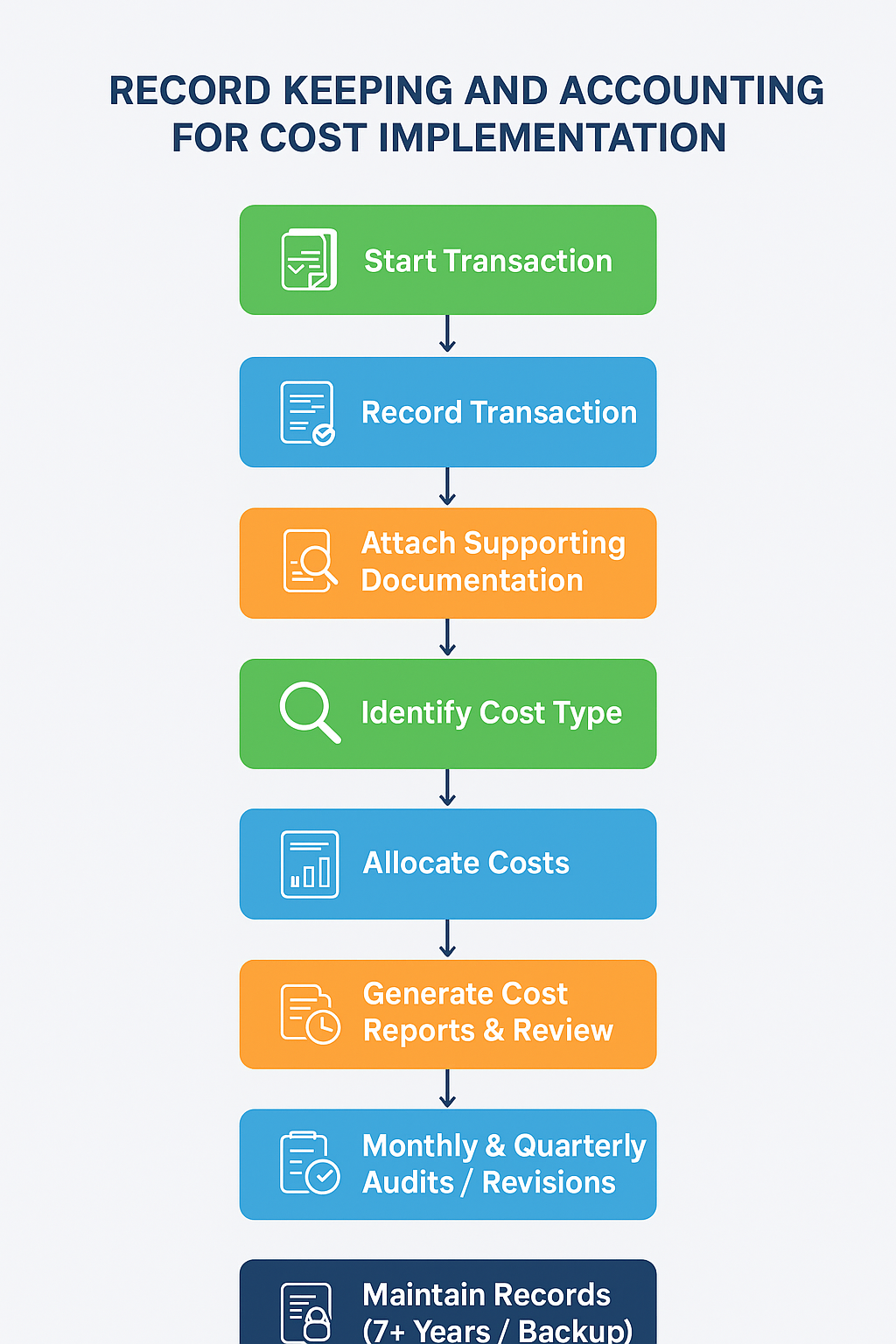
3. Steps in Document Creation
Requirement Analysis
Identify which documents are required under ISO 9001.
Define frequency, retention period, and responsible person.
Template Creation & Standardization
Develop templates aligned with ISO 9001 guidelines.
Ensure uniformity in headers, approval blocks, and version control.
Data Collection
Collect raw data from accounting entries, invoices, payroll systems, and cost centers.
Document Drafting
Populate templates with accurate data.
Include supporting evidence (receipts, audit logs).
Internal Review & Approval
Supervisor or accounting manager reviews accuracy.
ISO compliance check for format, completeness, and traceability.
Finalization & Distribution
Store in QMS system or document control software.
Provide access to authorized personnel.
Retention & Archiving
Follow ISO 9001 retention guidelines (e.g., financial records typically 7 years).
Track revisions and updates using version control.
4. Cost Analysis Components Cost Component Description Estimated Cost Labor Costs Time for accountants, document control personnel, and reviewers to create, review, and approve documents $30–$70/hr per person Software & Tools Accounting software, document management systems, template creation tools $100–$500/month Training Costs ISO 9001 training for accounting staff and document controllers $200–$1000 per employee Printing & Office Supplies Paper, ink, binders, folders for physical copies $0.10–$1 per document Audit & Compliance Costs Internal audits for document verification, external ISO audits $500–$2000 per audit cycle Time Delay Costs Cost of revisions, error correction, or non-compliance Variable, depends on error impact Archiving & Storage Digital or physical storage solutions $50–$200/month
Notes:
Labor cost is usually the largest factor.
Digital document management can reduce physical costs and improve traceability.
Compliance failures (e.g., missing or inaccurate records) can result in fines or rework costs, often exceeding initial creation costs.
5. Cost-Saving Recommendations
Use Digital Templates – Reduces printing and manual entry errors.Automate Data Capture – Integrate accounting software with document management systems.Centralize Document Control – One system for access, versioning, and audit trail.Staff Training – Invest in ISO 9001 compliance training to reduce revisions and audit findings.Regular Review Cycles – Prevent accumulation of outdated or redundant documents.
6. Example: Monthly Document Creation Cost (Small Company) Item Quantity/Time Unit Cost Total Cost Accountant labor 40 hours $40/hr $1,600 Document control review 8 hours $35/hr $280 Software subscription 1 month $200 $200 Printing & Supplies 50 documents $0.50 $25 ISO training amortized 1 month $100 $100 Total $2,205
7. Conclusion Accounting document creation for ISO 9001 compliance involves labor, software, training, and review costs . Effective planning, digital automation, and template standardization reduce overall cost and improve efficiency while maintaining compliance. Proper record-keeping supports audits, financial accuracy, and ISO certification readiness.